Right Hand Rule Moment Vector

Moments add together as vectors.
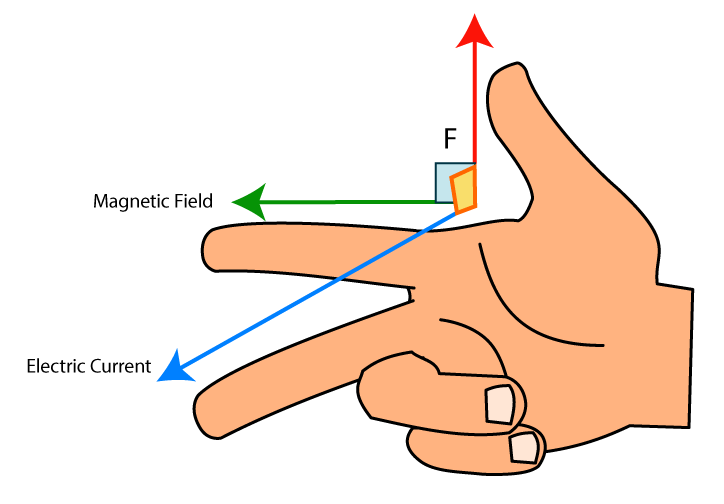
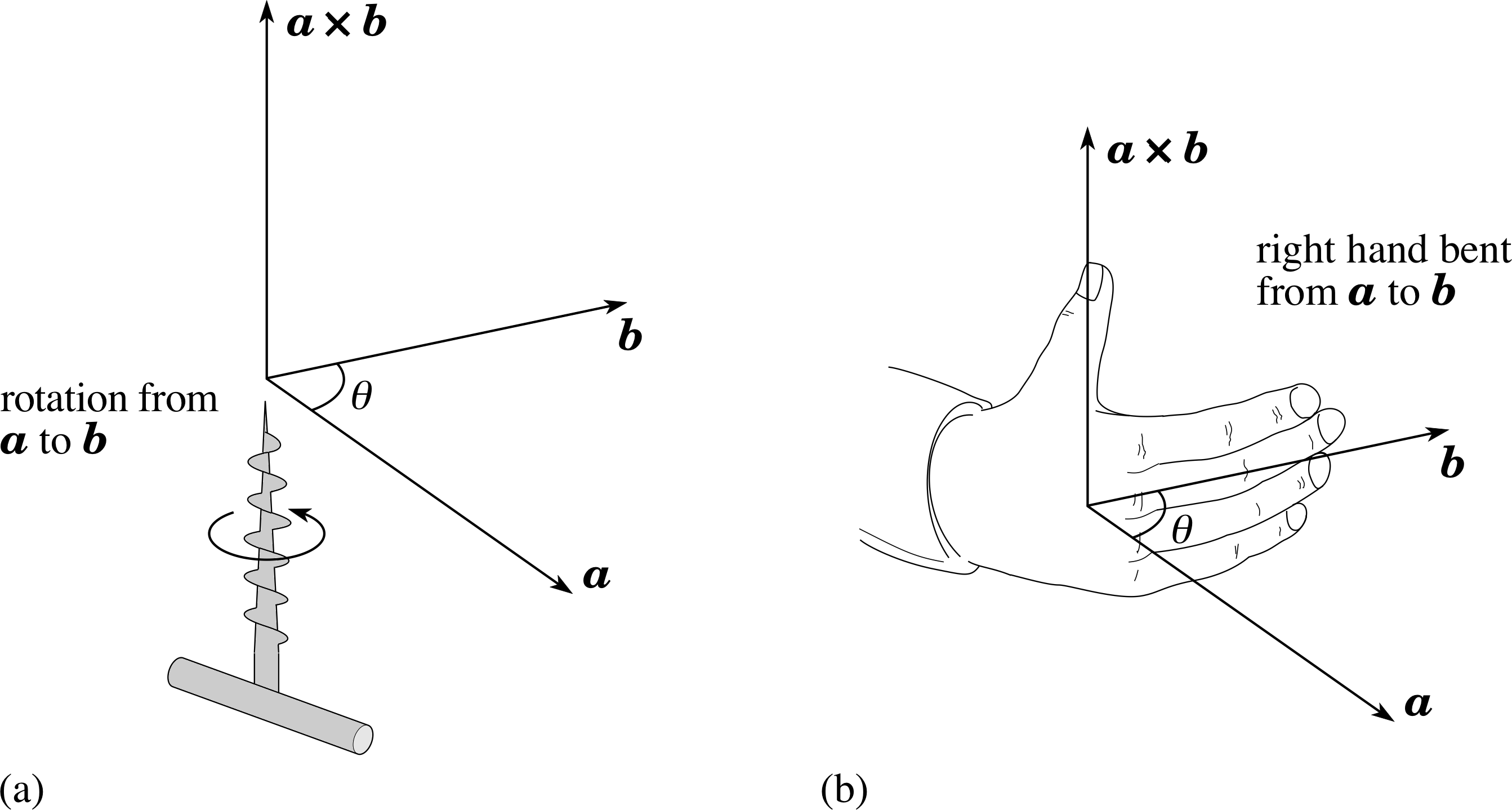
Right hand rule moment vector. The direction of your thumb is. Direction of the moment in 2 d. Right hand rule the ordinary or dot product of two vectors is simply a one dimensional number or scalar. Fingers are to point in the direction of the first vector and are curled towards the second vector.
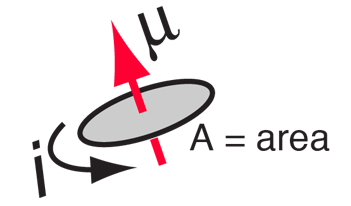
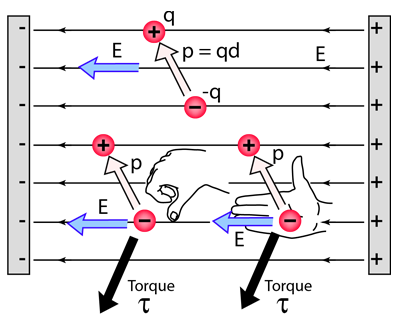
Part of the torque calculation is the determination of direction. The vector is the dipole moment vector. Recall the use of the right hand rule in torque calculations. Ampère s right hand grip rule also called right hand screw rule coffee mug rule or the corkscrew rule is used either when a vector such as the euler vector must be defined to represent the rotation of a body a magnetic field or a fluid or vice versa when it is necessary to define a rotation vector to understand how rotation occurs.
Select a positive direction ccw or cw then calculate each moment and add them using the proper sign for each term. The moment vector is pointing in the positive z direction. What factors does it depend on. The direction of the moment is given by the right hand rule.
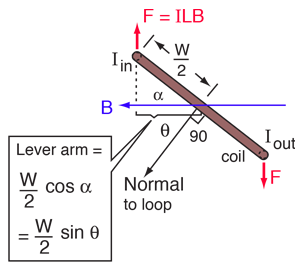
It is based on the following sign convention for an xyz coordinate system as shown below. So the fingers would point to in the same direction as the moment arm and are curled to the direction of the force clockwise. The result of rcross fwill give us the moment vector. Under which circumstances will the loop experience a nonzero net torque.
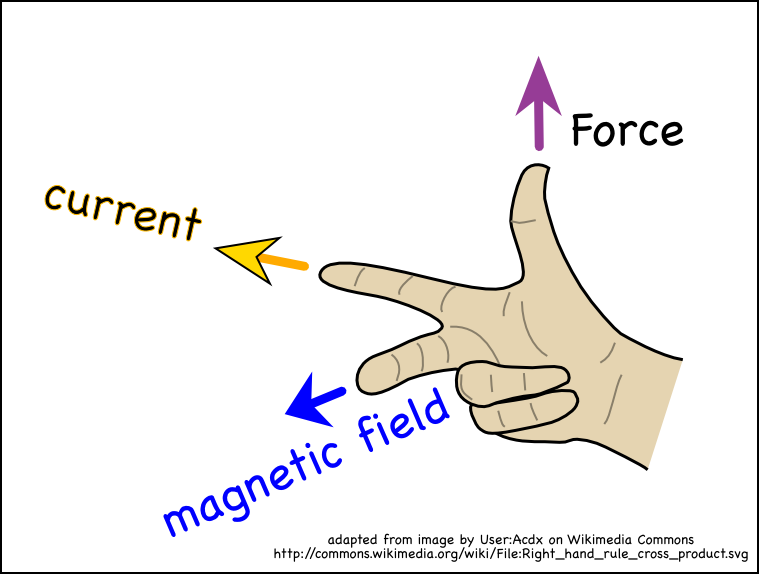
Using the right hand rule to find the direction of the cross product of two vectors in the plane of the page. Right hand thumb rule. The right hand rule is used extensively in this simulation. Under which circumstances will the loop experience a net upward force.
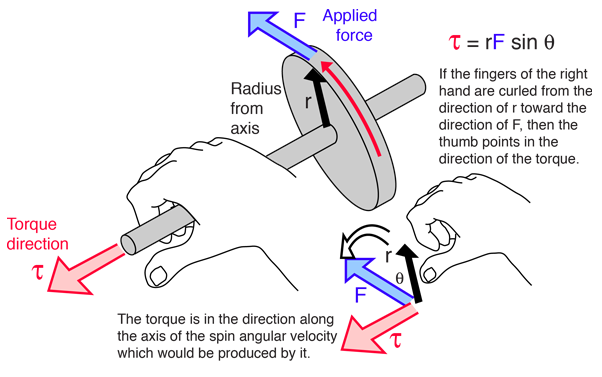
Right hand rule for torque torqueis inherently a vector quantity. The direction is perpendicular to both the radius from the axis and to the force. Counter clockwise ccw is out of the page clockwise cw is into the page. Verify that each of the four force vectors shown here follows the right hand rule.
In contrast the cross product of two vectors results in another vector whose direction is orthogonal to both of the original vectors as illustrated by the right hand rule. Right hand rule to determine if the moment is going clockwise or counterclockwise about that axis.










/torque-56a72bd25f9b58b7d0e78a8d.png)